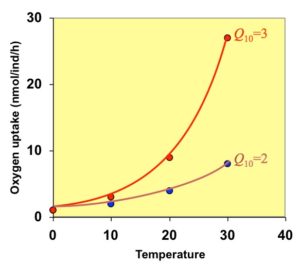
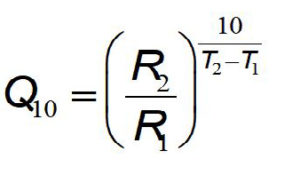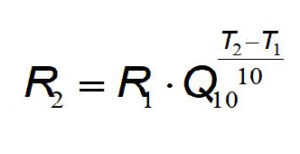The Q10 defines the temperature coefficient. Q10 explaines the factor by which the rate of a reaction (R) increases for every 10-degree rise in temperature (T). Most biological systems got a Q10 between 2-3. There are variations between during different developmental stages and between species. Q10=2 means that the rate of the reaction doubles for each 10°C rise in temperature. Q10=3 means that the reaction rate triple with each 10°C rise in temperature.
The reactions who is strongly dependent on the temperature (larger Q10) indicates a larger temperature sensitivity. Small temperature differences have a large impact on the reaction.
In respirometry, the reaction (R) measured is the oxygen consumption [O2] in nmol (nmol/ind/h).
Calculations using Q10
The temperature coefficient (Q10) is calculated by measuring the rate of a reaction (R) at two different temperatures in Celsius degrees or kelvin and where T1<T2. This yield an R1 at T1 and R2 at T2. The Q10 equation is then used to estimate the Q10 for the process.
The lab report
Use Equation 1 to calculate Q10 using your own data from the lab.
Practice on your own!
The Q10=4.5 for zebrafish embryo and larvae from 24 hours after fertilization.
Rewrite the equation 1 to solve it for R1 and R2. Use for the oxygen uptake (R1) at the rearing temperature of 28°C at 5.82 nmol/ind/h. Remember T1<T2 when solving for the different temperatures.
Calculate the oxygen uptake for your data at 24°C and 32°C.