Closed respirometry is the method in this lab module. The oxygen will be measured using the FireStingO2 optical oxygen meter. The oxygen meter is operated from a computer using the Oxygen Logger software.
The software is calibrated using blank vials. This video introduces you to the software FireStingO2 step-by-step. When the calibration is completed, the fish eggs and -larvae are pipetted into thevials. These vials containing fish are kept in a water bath to ensure stable temperature while the oxygen content in the vials is measured in real-time.This video introduce you to the practical skills in the lab.
Below you will find a step-by-step protocol for the closed respirometry.
Preparation
- For the incubation water, prepare a beaker with clean incubation water that is allowed to acclimate to test temperature.
- Make sure that all equipment (incubation vials) are also acclimated to the test temperature.
Calibration
- Prepare Oxygen saturated (100%) water at 28°C by shaking half-filled bottles with incubation water. Open lids several times to let in new O2 saturated air.
- Fill the 4 mL respiratory vials (chambers) with oxygen-saturated water (100%).
- Connect the adapters to the vials and then connect the fibre cables to one of the four input channels on the FireStingO2 interface.
- At this stage be careful and handle the sensors very carefully!
- Also, prevent any light from entering the fibre cables since this will possibly cause photo-bleaching (i.e. signal drift).
- Next, connect the FireStingO2 USB cable to the computer. The FireStingO2 logo blinks indicating a successful connection.
- Open the Oxygen Logger software (shortcut on PC-desktop).
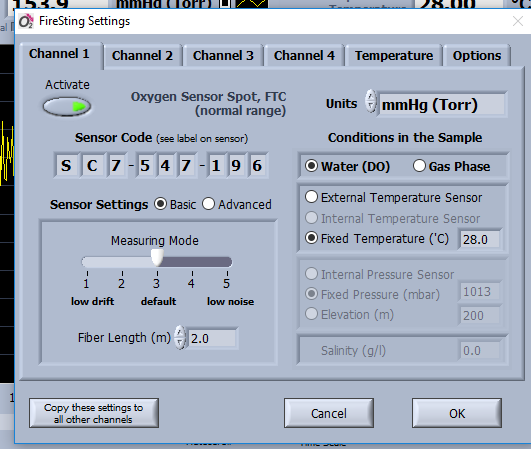
- Adjust Settings (Figure 1).
- Enter the sensor code for each input channel (given on the black bag of the vials).
- Adjust the setting according to environmental conditions in the experiment: Water, oxygen unit, temperature, salinity.
- Put the vials in a water bath (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Respiratory vials are immersed in a water bath to provide a constant temperature during the experiment. - Calibrate each of the four channels in Pyro Oxygen Logger. Use “One-point calibration in water or humid air” (Figure 3).
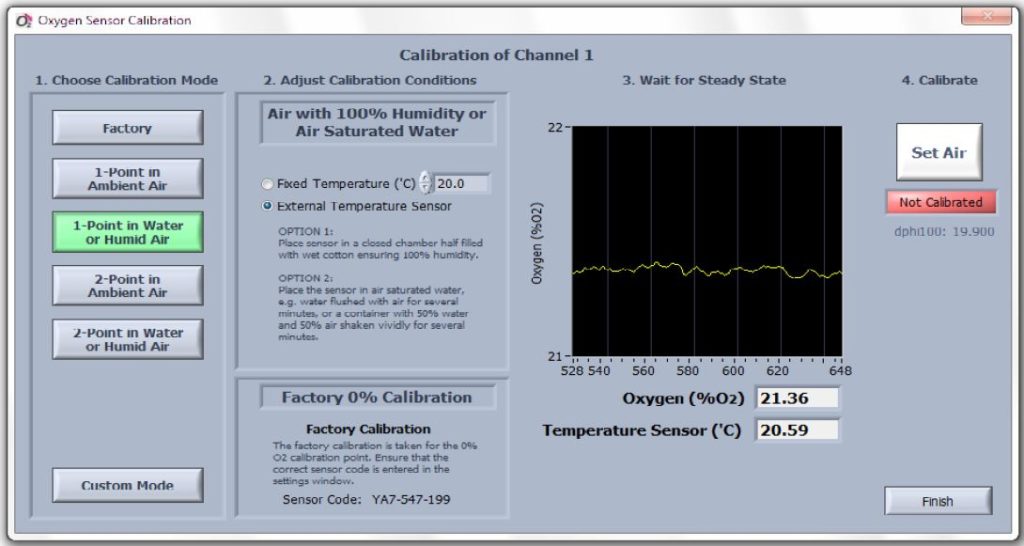
Figure 3: performing 1-point calibration in water or humid air. - Double check the sensor code of the vials.
- Set the external temperature to the test temperature.
- Press “Log to File” This will open a new file in the .txt-format.
- Save the file in the Experimental Folder.
- Save the log file (.txt file). Adjust the logging parameter (how often data is sampled (e.g. 1 time per second or 1 time per minute).
- Press “Start” to start regular data logging.
Preparation of eggs/larvae
- Check the egg or larva. Remove any dead or abnormal egg/larva (Figure 4, 5, 6 and 7).
- Make sure to minimise temperature fluctuations in the handling process.



Measurement
- Once the calibration is finished, perform measurement of the blank vials and save the data.
- Take the vials out of the water bath and add eggs/larvae into the vials.
- Setup: 3 vials filled with eggs/larvae, 1 blank (control).
- Make sure all vials are filled with water.
- Add egg/larva per non-blank vial.
- Minimize the amount of water included during transfer of larvae to the vials.
- Before closing the lid: avoid air bubbles in the vials (important)!
- Note the number of individuals per vial.
- Place the vial back in the water bath.
- Note the time when the incubation starts.
- Start measuring for 30 minutes.
- Fish egg and -larvae are immobile/inactive swimmers and will stay as a "cell layer" in the bottom of the vials. This can lead to oxygen consumption only in the bottom and create an oxygen gradient in the water (lower oxygen at the bottom, higher oxygen near the lid). Before ending the experiment, gently shake with the eggs/larvae the vials to get the correct readout of oxygen consumption (Figure 6)!
- Stop the measurement in the Oxygen Logger software after a certain time frame or drop in oxygen level.
- Take the vials out of the water bath.
- Empty the vial in a petri dish. Note the number of fish eggs/larvae, and the number of dead eggs/larvae.
- Clean the lab.